



Welcome to the captivating journey of unraveling the power of collagen! This article will delve into the depths of collagen’s potential, exploring how it holds the key to youthful skin and strong joints.
Collagen, the fundamental protein in our bodies, plays an extraordinary role in maintaining the integrity and strength of our connective tissues. As we age, collagen production naturally declines, making collagen management an essential aspect of our overall health and well-being.
Join me as we embark on an exciting journey to unveil the mysteries of collagen. Together, we will explore its vital significance in our bodies and discover the remarkable ways it can help us achieve youthful skin and robust joints.
Understanding Collagen
Collagen is a critical protein that provides strength, structure, and support to various tissues in the body, including the skin, tendons, ligaments, cartilage, and bones. It plays a vital role in maintaining the structural integrity of these tissues, promoting skin elasticity, joint flexibility, and overall health.
The importance of collagen lies in its numerous functions and contributions to our overall health:
Structural Support
Collagen acts as a foundational component, giving tissues and organs their shape and strength. It provides a framework for cells and other molecules to adhere to, ensuring the integrity and stability of the body’s structures.
Skin Health
Collagen plays a vital role in maintaining the elasticity, firmness, and hydration of the skin. It helps to smooth out wrinkles, improve skin texture, and promote a youthful appearance.
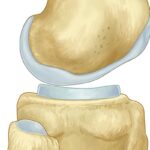
Joint and Bone Health
Collagen is essential for healthy joints, as it helps maintain the integrity of cartilage, which cushions the joints and enables smooth movement. It also contributes to bone strength and density, supporting overall skeletal health.
Wound Healing
Collagen is involved in the process of wound healing by providing a framework for new tissue growth and promoting the regeneration of damaged skin.
Organ Support
Collagen provides support and structure to internal organs, such as the liver, kidneys, and heart, helping them maintain their shape and function properly.
Overall, collagen is a fundamental protein in the body, playing a crucial role in maintaining tissue integrity, supporting skin health, ensuring joint flexibility, and contributing to overall well-being.
Types of Collagen
Collagen is a diverse family of proteins, and different types of collagen serve specific functions in the body. Here are some of the main types of collagen and their respective functions:
Type I Collagen
This is the most abundant type of collagen in the body and is found in the skin, tendons, ligaments, bones, and teeth. It provides tensile strength and resistance to stretching, contributing to the structural integrity of these tissues.
Type II Collagen
Type II collagen is mainly present in cartilage, which covers the ends of bones in joints. It provides structure and elasticity to cartilage, enabling smooth joint movement and shock absorption.
Type III Collagen
This type of collagen is often found alongside type I collagen and provides support to hollow organs, such as blood vessels, the uterus, and the intestines. It also plays a role in wound healing and is commonly found in early-stage connective tissue during the healing process.
Type IV Collagen
Type IV collagen is a major component of the basement membrane, a specialized extracellular matrix that provides structural support to various tissues and organs. It is present in the skin, blood vessels, and the filtration system of the kidneys.
Type V Collagen
This type of collagen is involved in the formation of cell surfaces, hair, and the tissue surrounding cells. It contributes to the structural stability of these tissues and plays a role in regulating cell function.
These are just a few examples of the many types of collagen found in the body, each with its unique structure and function. The diversity of collagen types highlights its versatility and importance in supporting various tissues and maintaining overall tissue health.
Collagen Synthesis & Collagen Production
Collagen synthesis refers to the process by which the body produces new collagen molecules. It is a complex biological process that involves the production, modification, and assembly of collagen proteins.
During collagen synthesis, specialized cells called fibroblasts produce and secrete collagen precursors known as procollagens. These procollagens then undergo several enzymatic steps to form mature collagen molecules. These molecules are then organized into a network of fibers that provide structural support to various tissues in the body.
Factors affecting collagen production
Unfortunately, as we age, collagen synthesis gradually declines. This decline is primarily due to a combination of intrinsic and extrinsic factors:
Intrinsic Factors:
- Genetic Factors: Genetic variations can influence the rate of collagen synthesis and its degradation in the body.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, such as decreased estrogen levels during menopause, can contribute to a decline in collagen production.
- Natural Aging Process: As part of the natural aging process, the body’s ability to produce collagen decreases over time.
Extrinsic Factors:
- Sun Exposure: Overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun can accelerate collagen breakdown and inhibit collagen synthesis.
- Lifestyle Choices: Unhealthy lifestyle habits such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, poor nutrition, and inadequate sleep can negatively impact collagen production.
- Environmental Factors: Pollution, stress, and certain medications can also affect collagen synthesis and contribute to its decline.
Together, these factors can disrupt the delicate balance between collagen production and degradation in the body, leading to a gradual decrease in collagen levels over time.
Understanding the factors that influence collagen production can help us make informed choices to support and optimize collagen synthesis. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, protecting our skin from sun damage, and nourishing our bodies with proper nutrition, we can potentially slow down the natural decline of collagen and promote overall collagen health.
Conclusion
As we conclude this part of our article on “Unveiling the Power of Collagen: The Key to Youthful Skin and Strong Joints,” we have journeyed through the significance of collagen, its role in the body, and the factors that influence collagen production. We now have a deeper understanding of the essential nature of collagen in maintaining tissue integrity, promoting skin health, and supporting joint function.
In Part 2, we will continue our exploration by delving into The Role of Collagen in Skin Health. We will uncover the remarkable ways collagen enhances skin elasticity, helps achieve a youthful complexion, and reduces the appearance of wrinkles. Get ready to discover the secrets behind collagen’s transformative power in rejuvenating and nourishing our skin. So, stay tuned as we unravel the fascinating world of collagen in Part 2 of our article.
© 2023 Tanushree Jain
