In our enlightening exploration, “The Art of Success: Harnessing NLP for Personal Transformation”, we delved deep into the core principles and transformative techniques of Neuro-Linguistic Programming (NLP), this next installment takes a focused look at a challenge many of us face—Anxiety.
Our aim is to arm you with a toolkit of actionable NLP strategies for managing and reducing anxiety, opening doors to newfound mental freedom and well-being.
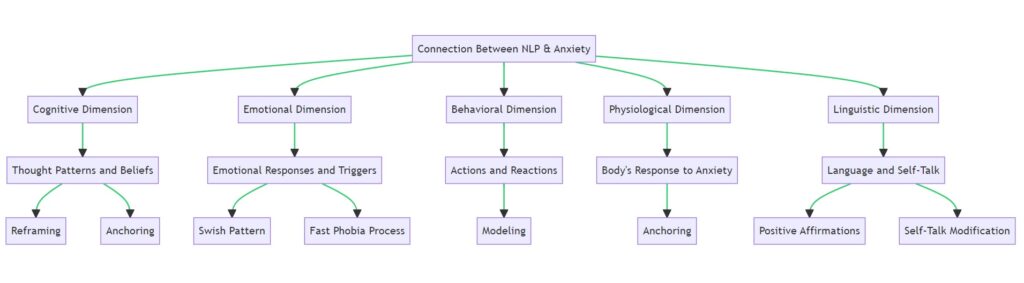
The Connection Between NLP and Anxiety
Neuro-Linguistic Programming (NLP) offers a set of tools and techniques that allow individuals to modify their thought patterns, behaviors, and emotional responses. Anxiety often stems from negative thought patterns that can spiral out of control. NLP techniques aim to identify and reframe these patterns, offering a way to manage anxiety effectively.
Cognitive Dimension: Thought Patterns and Beliefs
Anxiety often stems from negative or self-limiting thought patterns and beliefs. These thoughts can be repetitive, and intrusive, and can lead to a cycle of worry and fear. NLP techniques like “reframing” and “anchoring” aim to break this cycle by identifying the structure and language of these thoughts. By understanding how these thoughts are formed, individuals can dismantle them and replace them with more positive and empowering narratives.
Emotional Dimension: Emotional Responses and Triggers
Anxiety is also characterized by heightened emotional responses to certain triggers. NLP techniques such as “Swish Pattern” or “Fast Phobia Process” are designed to neutralize the emotional charge associated with these triggers. By altering the emotional response, individuals can reduce or even eliminate the anxiety associated with specific situations or memories.
Behavioral Dimension: Actions and Reactions
Anxiety often leads to avoidance behaviors, where individuals steer clear of situations that trigger their anxiety. NLP offers techniques like “Modeling” to replace the negative imagery and emotional responses associated with these situations with positive and empowering ones. This change helps individuals to engage in situations they would typically avoid, thereby altering their behavioral response to anxiety.
Physiological Dimension: Body’s Response to Anxiety
The body’s “fight or flight” response is often activated during anxious moments, leading to symptoms like rapid breathing and increased heart rate. NLP techniques such as “anchoring” can help individuals associate calming sensations with specific triggers, effectively reprogramming the body’s physiological response to anxiety-inducing situations.
Linguistic Dimension: Language and Self-Talk
The language we use in our internal dialogue can also contribute to anxiety. Phrases like “I can’t handle this” or “This is too much for me” can exacerbate feelings of anxiety. NLP focuses on altering this internal dialogue through techniques like “Positive Affirmations” and “Self-Talk Modification,” which can significantly impact how one experiences anxiety.
NLP provides a comprehensive approach to managing anxiety by addressing its cognitive, emotional, behavioral, physiological, and linguistic aspects. By applying NLP techniques tailored for each of these dimensions, individuals can achieve a more holistic management of their anxiety symptoms.
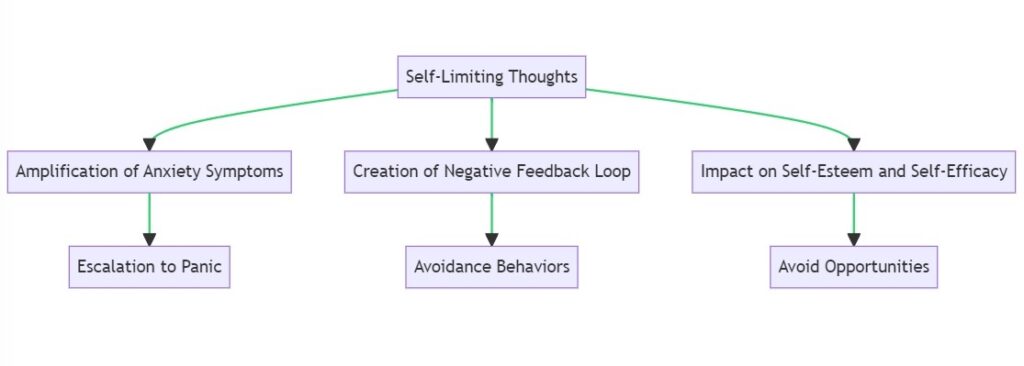
Importance of Managing Self-Limiting Thoughts in Anxiety
Self-limiting thoughts play a significant role in perpetuating anxiety. NLP provides the tools to identify, challenge, and change these thoughts, thereby reducing anxiety symptoms.
Amplification of Anxiety Symptoms
Self-limiting thoughts often serve as the fuel that amplifies anxiety symptoms. Thoughts like “I can’t handle this” or “Something bad is going to happen” can escalate a mild feeling of unease to full-blown panic. By identifying and managing these thoughts, you can significantly reduce the intensity of your anxiety symptoms.
Creation of a Negative Feedback Loop
Self-limiting thoughts can create a negative feedback loop where the thought exacerbates the anxiety, and the increased anxiety, in turn, reinforces the thought. This loop can be incredibly debilitating and can lead to avoidance behaviors, further entrenching the anxiety. NLP techniques can help break this loop by challenging the validity and utility of these self-limiting thoughts.
Impact on Self-Esteem and Self-Efficacy
Constantly entertaining self-limiting thoughts can erode your self-esteem and self-efficacy, making you less likely to engage in behaviors that could alleviate your anxiety. For example, if you constantly think, “I’m not good enough,” you may avoid opportunities that could prove otherwise. Managing these thoughts can restore your belief in your ability to cope with anxiety-inducing situations.
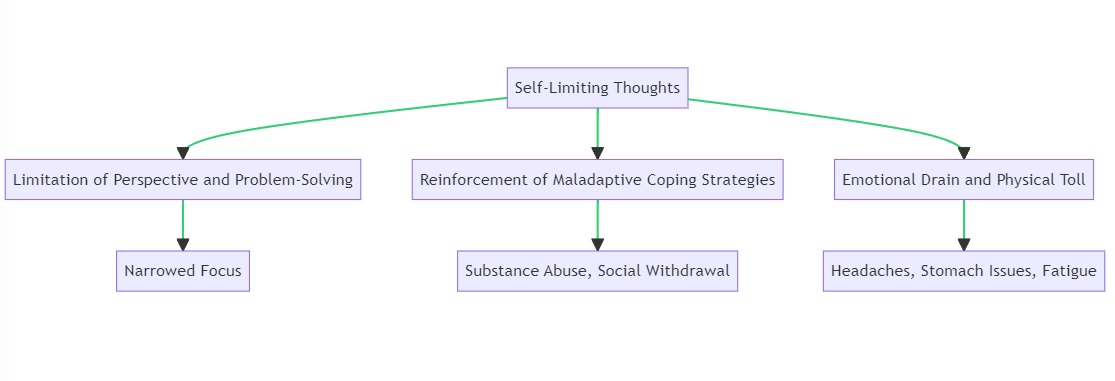
Limitation of Perspective and Problem-Solving
Self-limiting thoughts often narrow your focus and limit your ability to see alternative perspectives or solutions to problems. This narrowed focus can make the anxiety seem insurmountable. By managing these thoughts, you open up your cognitive space to explore different coping mechanisms and solutions, making the anxiety more manageable.
Reinforcement of Maladaptive Coping Strategies
When plagued by self-limiting thoughts, individuals often resort to maladaptive coping strategies like substance abuse, social withdrawal, or obsessive-compulsive behaviors. These strategies may offer temporary relief but usually exacerbate the problem in the long run. Managing self-limiting thoughts can pave the way for healthier coping mechanisms, such as cognitive restructuring, deep breathing, or positive visualization.
Emotional Drain and Physical Toll
The emotional weight of self-limiting thoughts can be draining and can even take a physical toll on your body, manifesting as symptoms like headaches, stomach issues, or chronic fatigue. By managing these thoughts, you can also alleviate the emotional and physical symptoms associated with them.
Managing self-limiting thoughts is not just a mental exercise but a comprehensive strategy that can have a profound impact on your emotional well-being, physical health, and overall quality of life. It’s an essential component in the holistic management of anxiety.
NLP Techniques for Managing Self-Limiting Thoughts
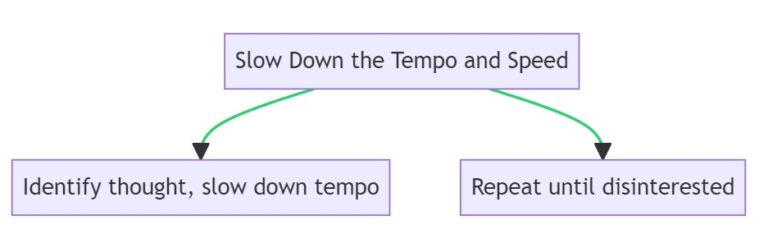
1. Slow Down the Tempo and Speed
How to Implement:
- Identify a recurring self-limiting thought.
- Consciously slow down the speed at which you think or say this thought.
- Repeat the thought at this slower pace until you feel disinterested or bored.
Slowing down the tempo of your thoughts allows you to disengage from the emotional charge they carry. Rapid thoughts can easily trigger emotional responses, but by slowing them down, you create space to observe them more objectively. This detachment can help you question the validity of these thoughts and reduce their impact.
2. Create Boredom Behind the Thought
How to Implement:
- Take the same self-limiting thought.
- Repeat it in a monotonous and unenthusiastic tone, either out loud or in your mind.
- Continue until the thought loses its emotional impact.
The goal is to make the thought so boring that it loses its power over you. When you repeat something enough times without emotional engagement, it becomes less interesting and impactful. This technique helps you disassociate from the emotional charge of the thought.
3. Change the Pitch
How to Implement:
- Think or say the self-limiting thought in a higher or lower pitch than your natural voice.
- Experiment with different pitches to find the one that makes the thought seem least threatening.
Changing the pitch alters the way you perceive the thought. A higher pitch might make it sound silly, while a lower pitch might make it sound less urgent. This change in perception can reduce the emotional weight of the thought.
4. Add an Echo
How to Implement:
- As you think or say the self-limiting thought, add an echo to each word.
- For example, if the thought is “I can’t do this,” it becomes “I, I, I can’t, can’t, can’t do, do, do this, this, this.”
Adding an echo disrupts the natural flow of the thought, making it harder to engage with emotionally. The repetition creates a sense of detachment from the thought, reducing its impact and making it easier to challenge its validity.
5. Put It into Past Tense
How to Implement:
- Change the self-limiting thought into the past tense.
- For example, “I can’t do this” becomes “I couldn’t do this.”
Putting the thought into the past tense helps you distance yourself from it. It creates a psychological separation, allowing you to consider that this was something you used to believe, not something that must be true now. This temporal shift can be empowering and can help you challenge the thought’s current relevance.
Each of these NLP techniques offers a unique approach to managing self-limiting thoughts, and they can be used in combination for a more comprehensive strategy. By applying these techniques, you can significantly reduce the power that self-limiting thoughts have over your emotional state, thereby managing your anxiety more effectively.
NLP Techniques for Anxiety Reduction
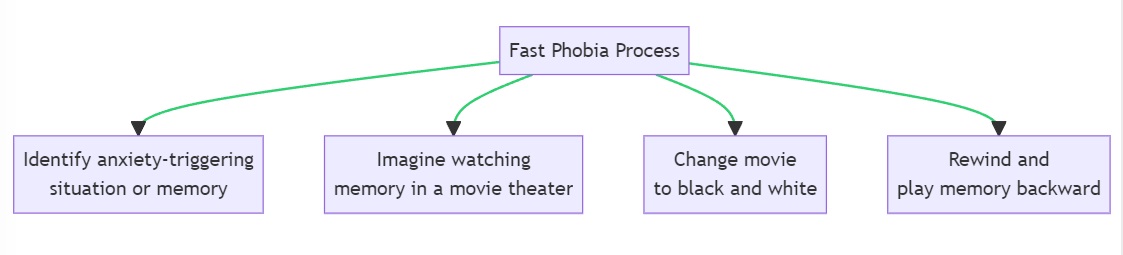
1. Fast Phobia Process
How to Implement:
- Identify the specific situation or memory that triggers your anxiety.
- Imagine you’re in a movie theater, watching this memory on a screen.
- Change the movie to black and white.
- Imagine a rewind button and play the memory backward multiple times.
The Fast Phobia Process is an NLP technique that aims to neutralize the emotional charge of a traumatic memory. By disassociating from the memory and altering its visual and emotional elements, you can reduce or eliminate the anxiety it triggers. Practice this technique in a quiet space where you can focus, and you may need to repeat the process multiple times for full effectiveness.
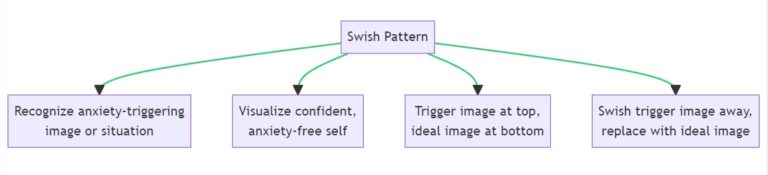
2. Swish Pattern
How to Implement:
- Recognize the image or situation that immediately precedes your feeling of anxiety.
- Visualize a confident, anxiety-free version of yourself.
- In your mind’s eye, see the trigger image at the top and the ideal image at the bottom.
- Quickly “swish” the trigger image away, replacing it with the ideal image.
The Swish Pattern is designed to replace a negative trigger image with a positive, empowering image. This substitution interrupts the usual pattern of anxiety and replaces it with a more positive emotional state. Make the ideal image as vivid as possible, incorporating all senses. The swishing action should be fast and decisive.
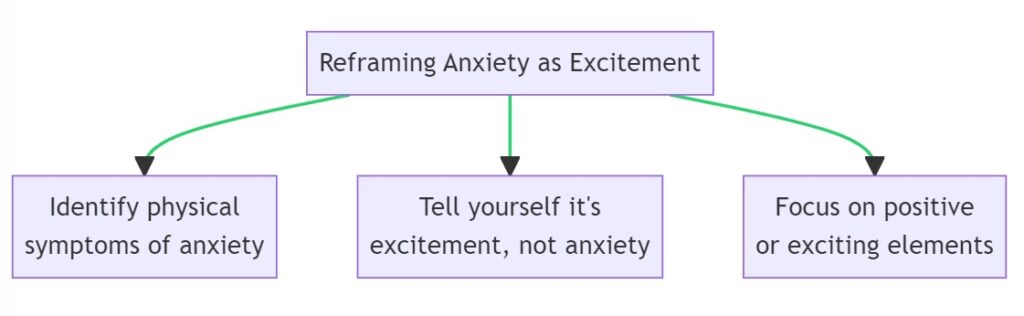
3. Reframing Anxiety as Excitement
How to Implement:
- When you start to feel anxious, identify the physical symptoms you’re experiencing.
- Consciously tell yourself that what you’re feeling is not anxiety but excitement.
- Shift your focus to the positive or exciting elements of the situation you’re in.
The physiological symptoms of anxiety and excitement are similar, such as rapid heartbeat and quick breathing. By consciously reframing your anxiety as excitement, you can change your emotional response to the trigger. Practice this reframe in less stressful situations first to make it easier to apply in more anxiety-inducing scenarios. Use positive affirmations to support the reframe.
Each of these advanced NLP techniques offers a unique approach to managing anxiety, and they can be used in combination for a more comprehensive strategy. By applying these techniques, you can significantly reduce the power that anxiety has over your emotional state, thereby managing your anxiety more effectively.
Closing Insights: The Holistic Benefits of NLP Techniques
As we close this chapter on NLP and anxiety management, it’s worth pondering the transformative power of the mind. The techniques we’ve explored are not just tools but keys to unlocking a life less burdened by anxiety. They challenge us to question the narratives we’ve accepted about ourselves and offer us the chance to rewrite those stories. So, as you go forward, remember that the mind is both the prison and the key to freedom. The choice of how to use it is entirely yours.
Conclusion
Neuro-Linguistic Programming (NLP) offers a multi-dimensional approach to managing anxiety, addressing its cognitive, emotional, behavioral, physiological, and linguistic aspects. By employing a range of NLP techniques, from reframing thought patterns to altering emotional responses, individuals can achieve a more holistic management of their anxiety symptoms. As we conclude, one question remains: Are you ready to unlock the transformative power of your mind to redefine your relationship with anxiety?
References
Bandler, R., & Grinder, J. (1979). Frogs into Princes: Neuro-Linguistic Programming. Real People Press.
Dilts, R. (1990). Changing Belief Systems with NLP. Meta Publications.
Andreas, S., & Andreas, C. (1989). Heart of the Mind: Engaging Your Inner Power to Change with Neuro-Linguistic Programming. Real People Press.
O’Connor, J., & Seymour, J. (1990). Introducing Neuro-Linguistic Programming: Psychological Skills for Understanding and Influencing People. Thorsons.
© 2023 Tanushree Jain